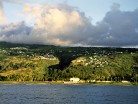Ua Huka is one of the Marquesas Islands, in French Polynesia, an overseas territory of France in the Pacific Ocean. It is situated in the northern group of the archipelago, approximately 25 mi (40 km). 42 km to the east of Nuku Hiva, at 8°54′S 139°33′W
Ua Huka is sometimes also found spelled Roohka or Ua Huna. The first Western navigator to sight the island was U.S. Navy Capt. Joseph Ingraham in 1791. He named the island “Washington Island” in honor of U. S. President George Washington, a name which was eventually extended to include all of the northern group of the Marquesas Islands. Other names for the island include Riou and Solide. See also Names of the Marquesas Islands.
The island is shaped approximately like a crescent, with its concave edge facing the south. The land area is approximately 83 km² (32 sq. mi.). The center of the island is a high plateau, deeply indented in places by narrow river valleys. The highest peak, Hitikau reaches an elevation of 857 m (2,812 ft). Much of the island’s native plant cover, which outside the valleys consists primarily of dry-land scrub, has been devastated by herds of feral goats and horses, which are estimated to number upwards of 3,000.
Ua Huka is a shield volcano that was emplaced between 2.2 and 2.4 million years ago. It is thought to have formed by a center of upwelling magma called the Marquesas hotspot.
Administratively Ua Huka forms the commune (municipality) of Ua-Huka, part of the administrative subdivision of the Marquesas Islands. This commune consists solely of the island of Ua Huka itself.
The administrative centre of the commune is the settlement of Vaipaee, on the southern side of the island.
The 2007 census showed a population of 571 inhabitants, residing in three villages: Vaipaee, Hane, and Hokatu.